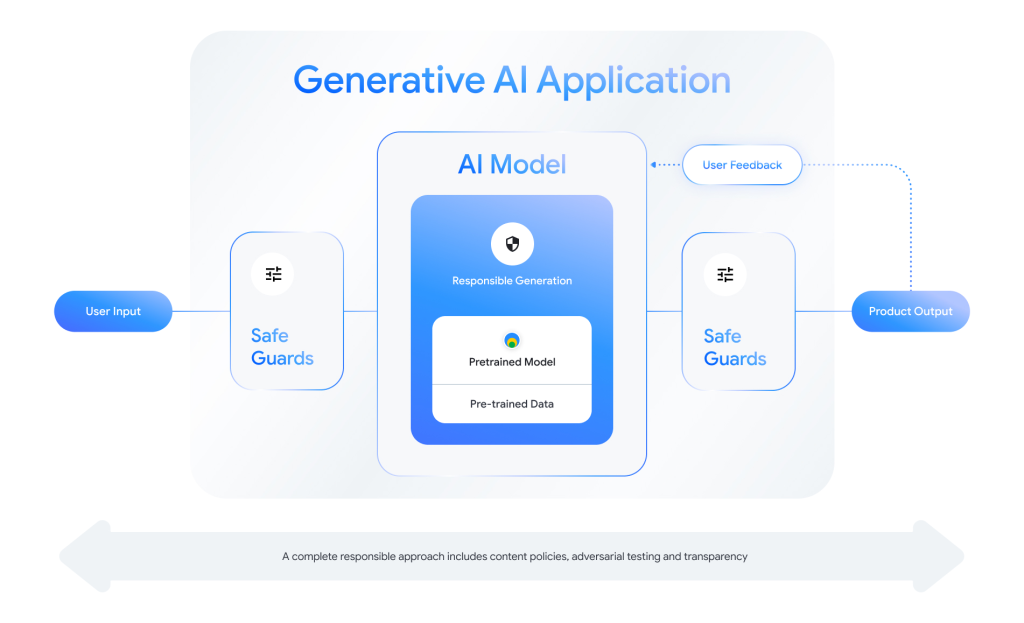
SAIF organizes AI security into four interconnected components
Each control is mapped onto the corresponding risks it can address, with the exception of Governance and Assurance controls, which apply universally to all risks and every stage of the AI development process.
Data
Privacy Enhancing Technologies
- Control: Privacy Enhancing Technologies
- Use technologies that minimize, de-identify, or restrict use of PII data in training or evaluating models.
- Who can implement: Model Creators
- Risk mapping: Sensitive Data Disclosure
Training Data Management
- Control: Training Data Management
- Ensure that all data used to train and evaluate models is authorized for the intended purposes.
- Who can implement: Model Creators
- Risk mapping: Inferred Sensitive Information
Training Data Sanitization
- Control: Training Data Sanitization
- Detect and remove or remediate poisoned or sensitive data in training and evaluation.
- Who can implement: Model Creators
- Risk mapping: Data Poisoning, Unauthorized Training Data
User Data Management
- Control: User Data Management
- Store, process, and use all user data (e.g. prompts and logs) from AI applications in compliance with user consent.
- Who can implement: Model Creators, Model Consumers
- Risk mapping: Sensitive Data Disclosure, Excessive Data Handling
Infrastructure
Model and Data Inventory Management
- Control: Model and Data Inventory Management
- Ensure that all data, code, models, and transformation tools used in AI applications are inventoried and tracked.
- Who can implement: Model Creators, Model Consumers (if storing models)
- Risk mapping: Data and Poisoning, Model Source Tampering, Model Exfiltration
Model and Data Access Controls
- Control: Model and Data Access Controls
- Minimize internal access to models, weights, datasets, etc. in storage and in production use.
- Who can implement: Model Creators, Model Consumers (if storing models)
- Risk mapping: Data Poisoning, Model Source Tampering, Model Exfiltration
Model and Data Integrity Management
- Control: Model and Data Integrity Management
- Ensure that all data, models, and code used to produce AI models are verifiably integrity-protected during development and deployment.
- Who can implement: Model Creators, Model Consumers (if storing models)
- Risk mapping: Data Poisoning, Model Source Tampering
Secure-by-Default ML Tooling
- Control: Secure-by-Default ML Tooling
- Use secure-by-default frameworks, libraries, software systems, and hardware components for AI development or deployment to protect confidentiality and integrity of AI assets and outputs
- Who can implement: Model Creators, Model Consumers (if storing models)
- Risk mapping: Data Poisoning, Model Source Tampering, Model Exfiltration, Model Deployment Tampering
Model
Input Validation and Sanitization
- Control: Input Validation and Sanitization
- Block or restrict adversarial queries to AI models.
- Who can implement: Model Creators, Model Consumers
- Risk mapping: Prompt Injection
Output Validation and Sanitization
- Control: Output Validation and Sanitization
- Block, nullify, or sanitize insecure output from AI models before passing it to applications, extensions or users.
- Who can implement: Model Creators, Model Consumers
- Risk mapping: Prompt Injection, Rogue Actions, Sensitive Data Disclosure, Inferred Sensitive Data
Adversarial Training and Testing
- Control: Adversarial Training and Testing
- Use techniques to make AI models robust to adversarial inputs (i.e. prompts) in the context of their use in applications.
- Who can implement: Model Creators, Model Consumers
- Risk mapping: Model Evasion, Prompt Injection, Sensitive Data Disclosure, Inferred Sensitive Data, Insecure Model Output
Application
Application Access Management
- Control: Application Access Management
- Ensure that only authorized users and endpoints can access specific resources for authorized actions.
- Who can implement: Model Consumers
- Risk mapping: Denial of ML Service, Model Reverse Engineering
User Transparency and Controls
- Control: User Transparency and Controls
- Inform users of relevant AI risks with disclosures, and provide transparency and control experiences for use of their data in AI applications.
- Who can implement: Model Consumers
- Risk mapping: Sensitive Data Disclosure, Excessive Data Handling
Agent/Plugin User Control
- Control: Agent/Plugin User Control
- Ensure user approval for any actions performed by agents/plugins that alter user data or act on the user’s behalf.
- Who can implement: Model Consumers
- Risk mapping: Rogue Actions
Agent/Plugin Permissions
- Control: Agent/Plugin Permissions
- Use least-privilege principle to minimize the number of tools that an agent/plugin is permitted to interact with and the actions it is allowed to take.
- Who can implement: Model Consumers
- Risk mapping: Insecure Integrated System, Rogue Actions